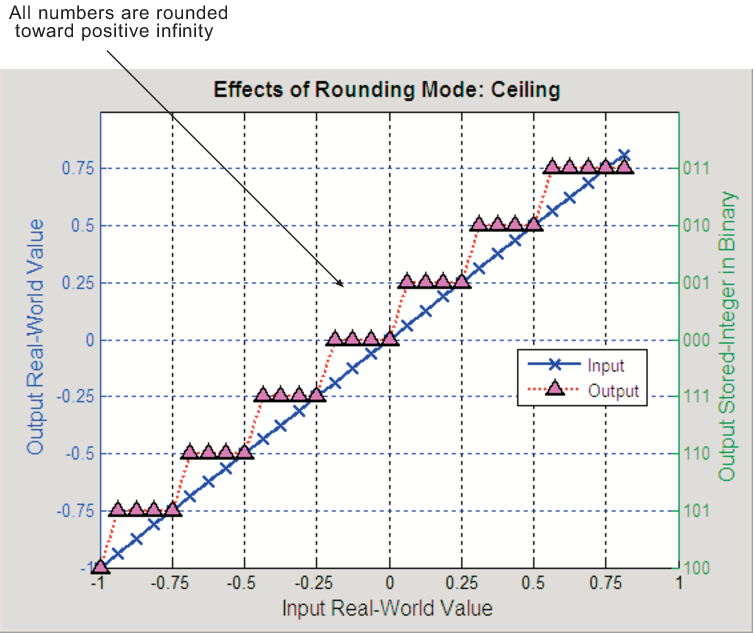
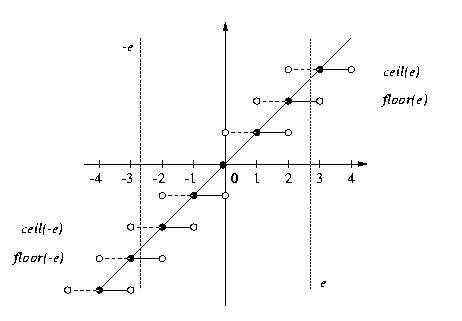How To Graph Floor And Ceiling Functions

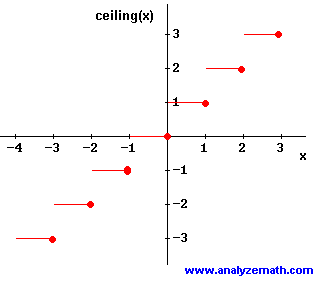
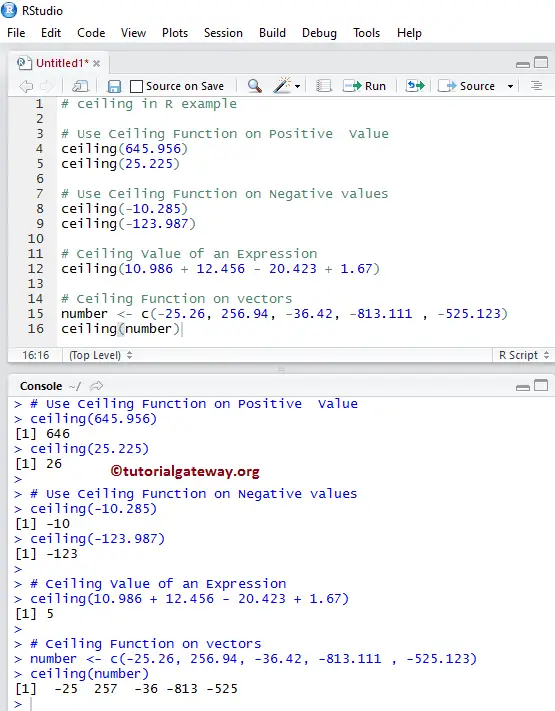
The ceiling function ceiling x is defined as the function that outputs the smallest integer greater than or equal to x.
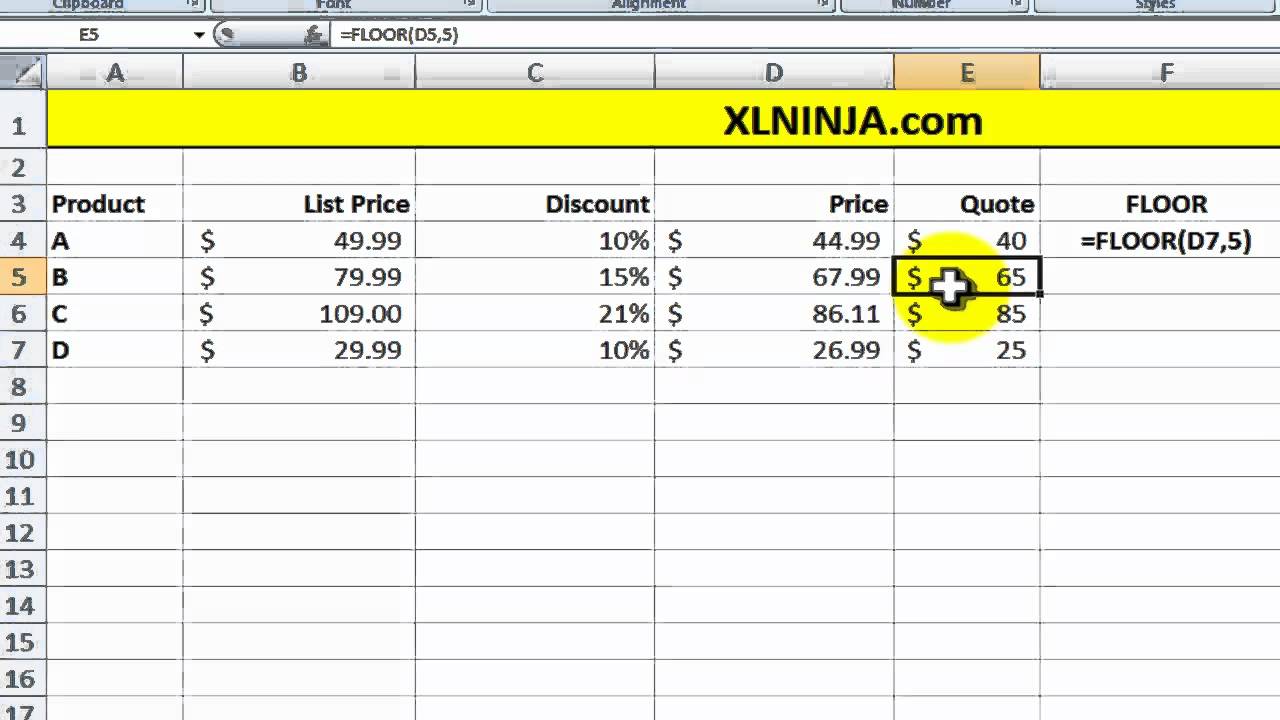
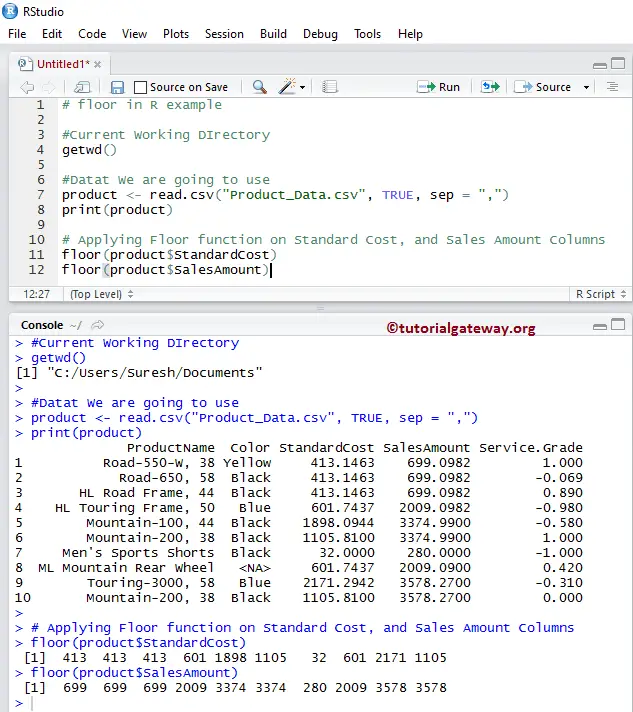
How to graph floor and ceiling functions. How do the floor and ceiling functions work. If 5 6 is a specified value then the floor value is 5 and the ceiling value is 6. Which leads to our definition. The table below shows values for the function from 5 to 5 along with the corresponding graph.
The greatest integer that is less than or equal to x. Floor greatest integer and ceiling functions. Click on the plot to clear the graph or drag again to clear and begin a new graph. Use your mouse to draw a function and view the graphs of and.
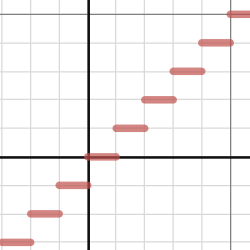
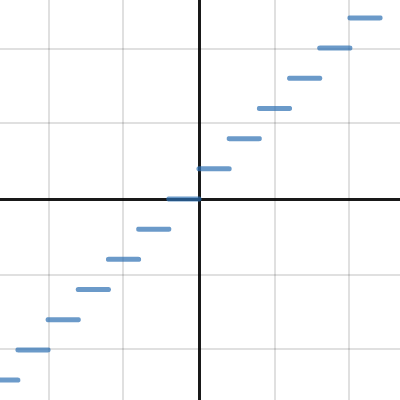
Choose the greatest one which is 2 in this case so we get. But for the floor function it is vice versa. The input to the floor function is any real number x and its output is the greatest integer less than or equal to x. Floor greatest integer and ceiling functions.
Notice that the function you draw always stays vertically between its floor and its ceiling. Floor x x examples floor 2 1 2 1 2 floor 3 3 3. To save your graphs. In the graph of ceiling function it has an open dot on the left and the solid dot on the right.
3 a b c π 0. The notation for the floor function is. Select what is displayed using the check boxes below the plot. Compare the graphs.
The table below shows values for the function from 5 to 5 along with the corresponding graph. By using this website you agree to our cookie policy. Floor greatest integer and ceiling functions. The greatest integer that is less than or equal to 2 31 is 2.
The floor function is a type of step function where the function is constant between any two integers. Free floor ceiling equation calculator calculate equations containing floor ceil values and expressions step by step this website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience. The least integer that is greater than or equal to x. It means that the solid dot on the left and the open dot on the right.