Ion Exchange Method For Water Treatment Ppt
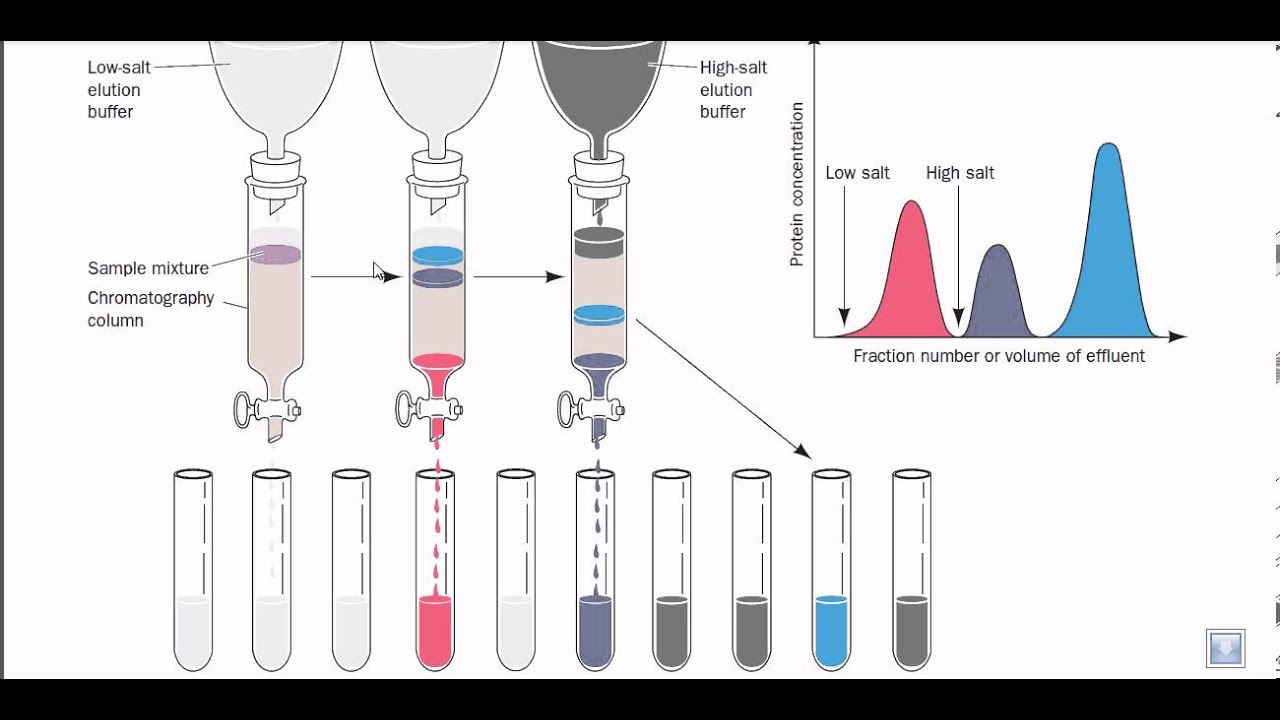
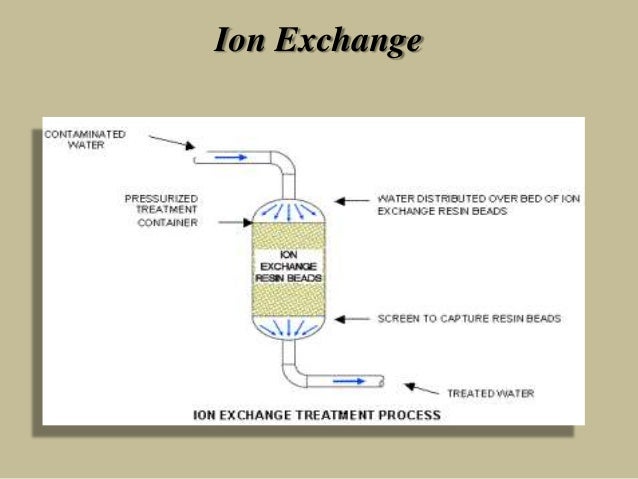
The ion exchange process percolates water through spherical porous bead resin materials ion exchange resins.
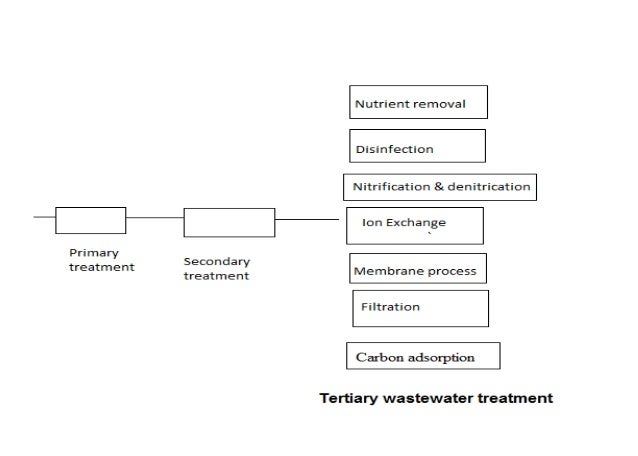
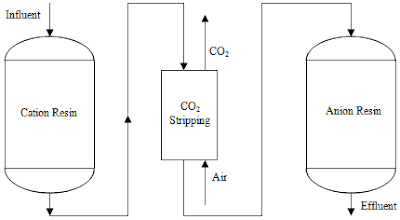
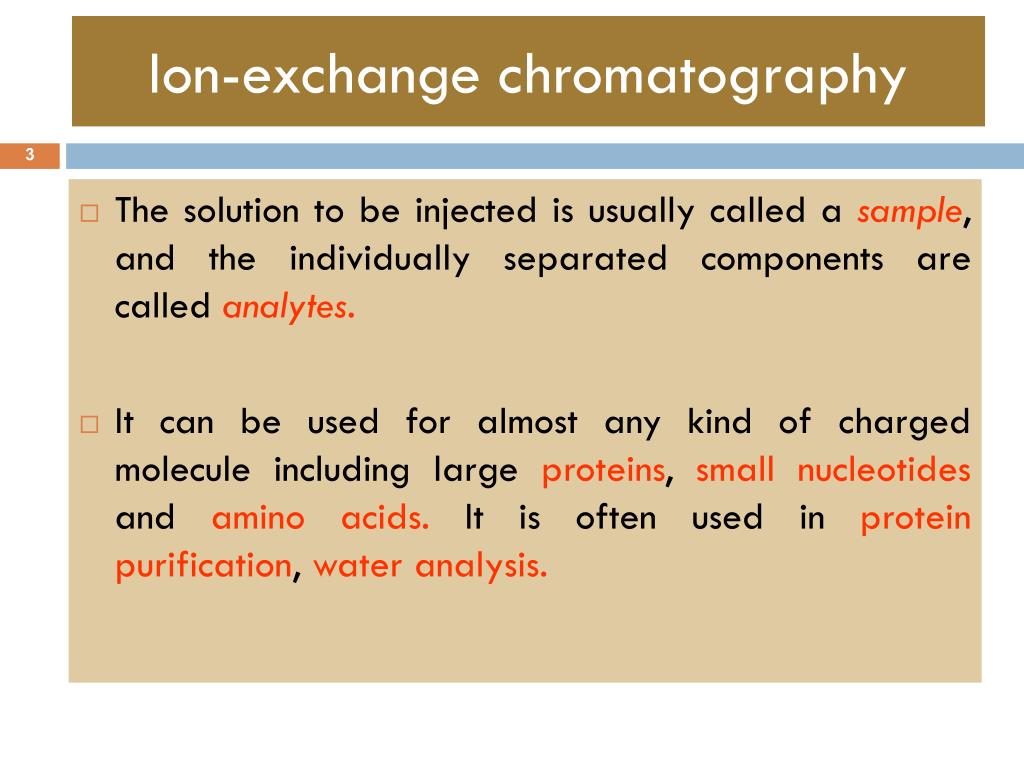
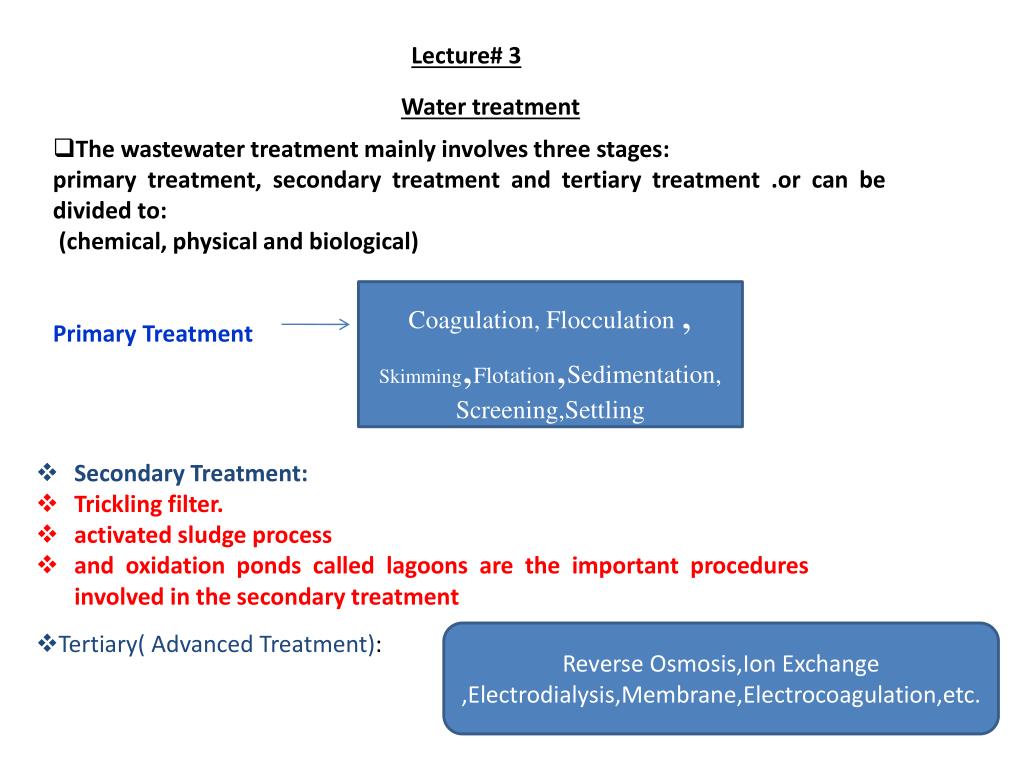
Ion exchange method for water treatment ppt. Treatment but chemical mechanism is ion exchange rather than adsorption. Ion exchange is a water treatment process commonly used for water softening or demineralization but it also is used to remove other substances from the water in processes such as dealkalization deionization and disinfection. 0 01 0 1 meq g. 10 ion exchange process 1.
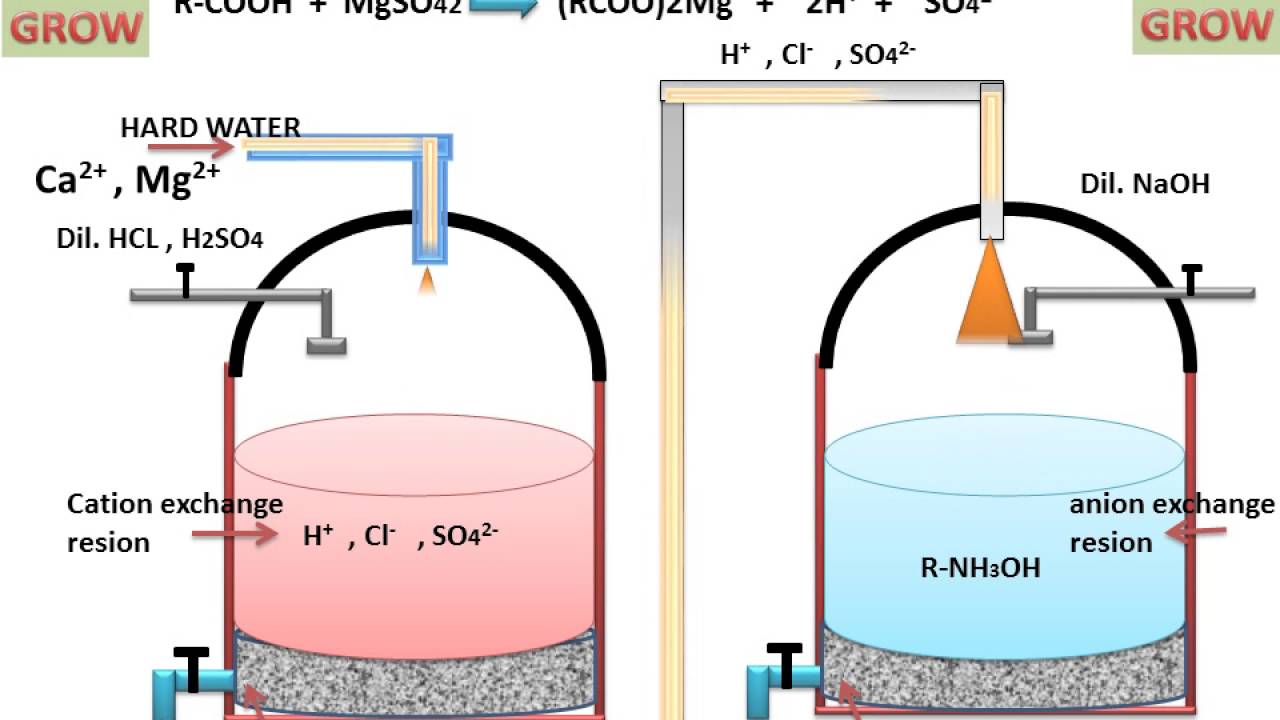
Structural types of ion exchange resins 1. In the ion exchange process sodium ions are used to coat an exchange medium in. Pellicular type with ion exchange film. Ions electrically charged atoms or molecules cations and anions can have one or more charges mostly 1 to 3 and can be made of one or.
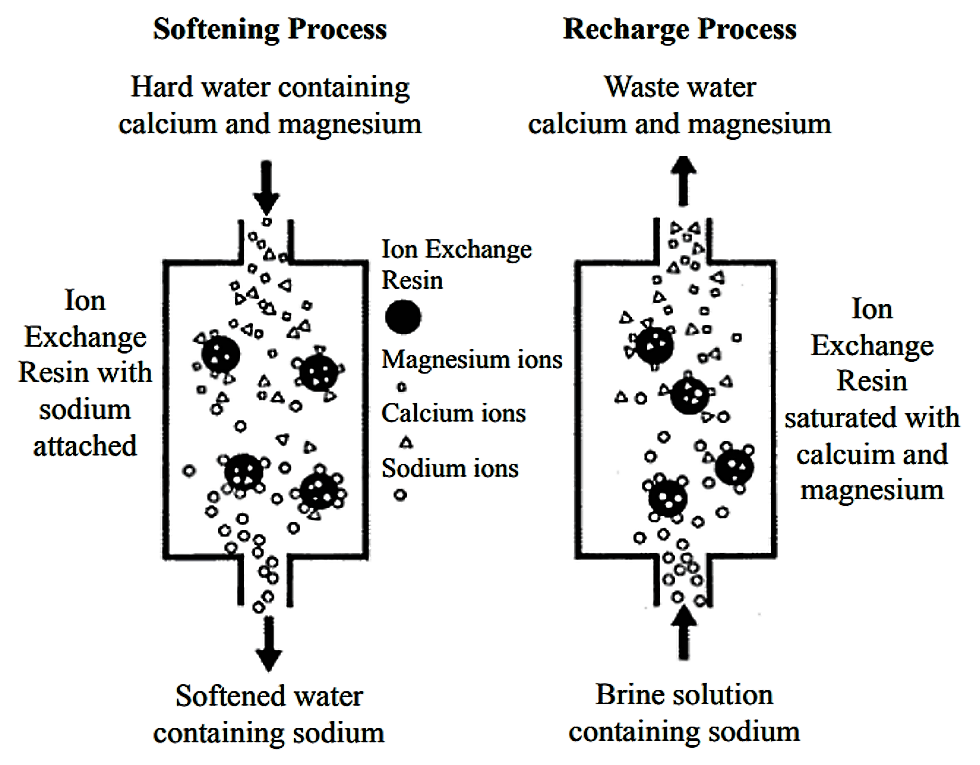
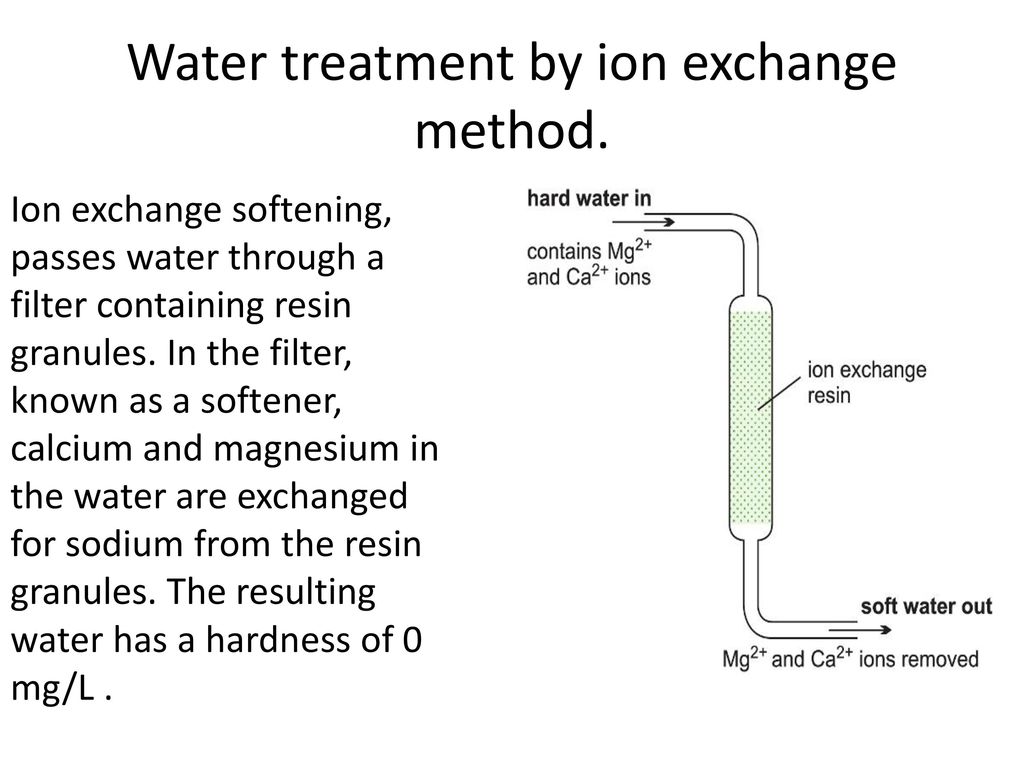
Skipton extension water quality educator bruce i. Water softeners usually use sodium na as the exchange ion. An ion exchange water softener exchanges the hardness minerals calcium and magnesium dissolved in water for sodium. These have very low exchange capacity ion exchange efficiency.
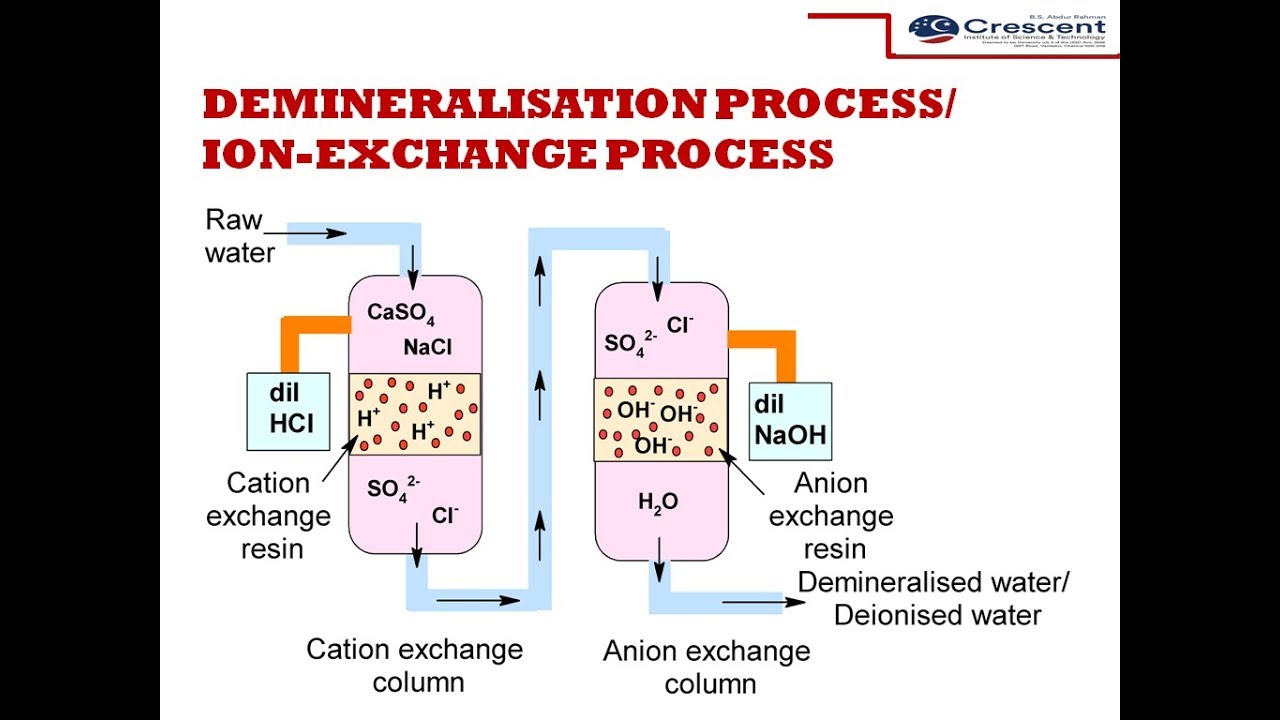
Ions in the water are exchanged for other ions fixed to the beads. In the ion exchange process a granular substance usually a resin that is coated with sodium or potassium ions comes into contact with water containing calcium and two positively charged sodium or potassium ions are exchanged released into the water for every calcium or magnesium ion that is held by the resin. The particles have a size of 30 40µ with 1 2µ film thickness. Water softening ion exchange sharon o.
Dvorak extension environmental engineering specialist the presence of calcium ca and or magnesium. Ion exchange is a water treatment commonly used for water softening or deminerialization and to remove other substances from water. Sodium ions are supplied from dissolved sodium chloride salt also called brine. Ion exchange process 2.
This soft mineral is contained on the softener resin beads and does not build up on surfaces as scale. The positive or negative ions fixed on these radicals are replaced by ions of the same sign in solution in the liquid in contact with them.
















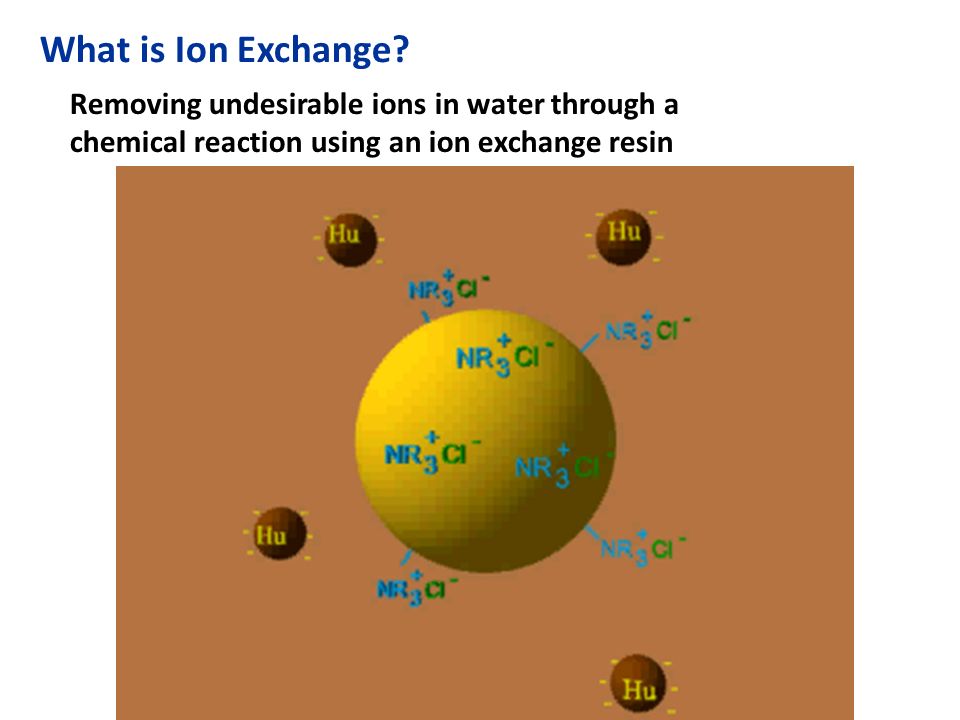









.jpg)